Reason to trust

How Our News is Made
Strict editorial policy that focuses on accuracy, relevance, and impartiality
Ad discliamer
Morbi pretium leo et nisl aliquam mollis. Quisque arcu lorem, ultricies quis pellentesque nec, ullamcorper eu odio.
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving world of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology, staking has emerged as a popular method for earning passive income. This process, integral to many proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchains, allows participants to lock their crypto assets in return for rewards. As decentralized finance (DeFi) grows, staking offers a lucrative alternative to traditional investment methods, attracting more investors seeking returns.
Understanding Staking
Staking is the process by which individuals lock their cryptocurrency, or “stake,” to support the security and operation of a blockchain network. By staking coins, participants help validate transactions and secure the network, earning rewards in return. This process is fundamental to PoS blockchains, such as Ethereum, Solana, and Cardano, and differs from proof-of-work (PoW) systems like Bitcoin, which rely on energy-intensive mining.
In PoS systems, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on a combination of factors, including the amount of cryptocurrency they have staked. This method does not require the specialized hardware needed for PoW mining, making it more accessible and environmentally friendly. In PoS, validators earn rewards through transaction fees and, in some cases, additional cryptocurrency, which incentivizes participation and enhances network security.
Benefits and Risks of Staking
Staking offers several benefits, including earning passive income through staking rewards, supporting network security, contributing to decentralization, and promoting energy efficiency compared to PoW mining. Additionally, most blockchain networks provide stakers with governance rights, allowing them to influence the network’s future direction.
However, staking is not without risks. These include the volatility of cryptocurrency prices, the potential for “slashing” penalties if validators violate network rules, centralization risks if a few validators control a large portion of the staked coins, and technical risks associated with maintaining validator nodes. Additionally, staked coins are typically locked up for a set period, which can limit liquidity and flexibility.
Types of Staking
There are various forms of staking, each catering to different preferences and levels of expertise:
- Direct Staking: This involves staking tokens directly from a personal wallet. It requires a certain amount of technical knowledge to manage and secure the staked assets.
- Staking through a Service Provider: Platforms like Allnodes offer staking services that handle the technical aspects on behalf of users, making it easier for non-technical investors to participate.
- Liquid Staking: This method allows users to stake their assets while still retaining liquidity through derivative tokens that can be traded or used in DeFi applications.
- Re-Staking: Platforms like EigenLayer enable users to re-stake their ETH or liquid-staked ETH to enhance network security and capital efficiency within the Ethereum ecosystem. Users can earn additional rewards in the form of EigenLayer points and Actively Validated Services (AVS).
The Mechanics of Staking
How Staking Works
Each PoS blockchain has its own staking currency, typically its native cryptocurrency, which is required to participate in the staking process. For example, Ethereum uses ether (ETH) as its staking currency. Users can stake their coins in various ways, depending on the amount of coins they hold, their level of technical expertise, and their desired level of control.
Options range from setting up and maintaining a validator node, which requires technical knowledge and offers the most control, to using staking-as-a-service platforms that take care of the technical aspects of a third-party provider. Cryptocurrency exchanges also offer staking services, allowing users to stake their holdings without needing to manage a validator node.
The Staking Process
To begin staking, users need to acquire a sufficient amount of crypto assets required to run a validator node on a certain network. For example, staking on Ethereum requires 32 ETH for a full validator node. Users with less than 32 ETH can participate in “pooled” staking through platforms like Rocket Pool or Stader.
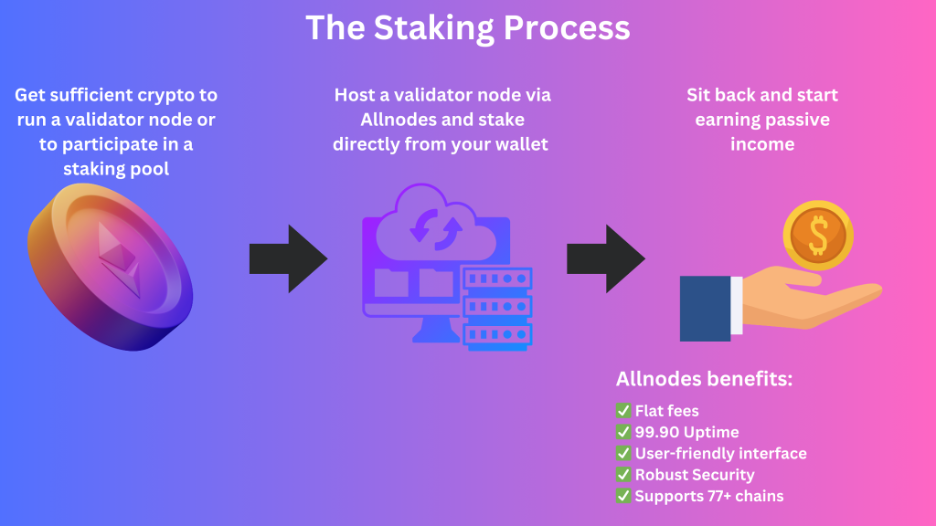
Example of Staking through a staking-as-a-service platform (via Allnodes)
Rewards Mechanism
Validators earn rewards for their participation, typically in the form of the network’s native cryptocurrency. The rewards are distributed based on the amount of stake and the length of time the tokens are locked up. For example, Ethereum staking currently yields an annual percentage yield (APY) of around 3.5%, depending on the staking conditions and market dynamics.
Maximizing Your Staking Rewards
To make the most out of staking, it is essential to adopt strategies that enhance returns and mitigate risks.
Monitoring Market Conditions
Staking rewards can vary with market conditions. Keeping an eye on these fluctuations and adjusting staking strategies accordingly can help maximize returns. Diversifying staked assets across multiple networks can also reduce risk and enhance earnings.
Compounding Earned Rewards
Re-investing earned rewards by staking them again can compound returns. This strategy, known as compounding, leverages the power of exponential growth to increase the total staking rewards over time.
Choosing a Staking Platform
Selecting the right staking platform is crucial for maximizing returns and minimizing risks. Here are some criteria to consider:
Security: Ensure the platform has robust security measures to protect staked assets.
Reputation: Look for platforms with a positive track record and good reviews from the community.
Fees: Compare the fees charged by different platforms, as they can significantly impact net returns.
Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface can simplify the staking process, especially for beginners.
Uptime: Uptime refers to the percentage of time a staking service is operational and actively participating in network activities. High uptime ensures that the staked assets are continuously engaged in validating transactions and earning rewards, ultimately maximizing the potential returns.
A Staking Platform: Allnodes
Allnodes stands out as a reliable staking service provider, offering a host of features that cater to both novice and experienced stakers.
Evidenced by the over 380 5-star reviews on Trustpilot, here are the features that make Allnodes a staking provider of choice.
- User-Friendly Interface: Allnodes provides an intuitive platform that simplifies the staking process.
- Robust Security Measures: The platform employs advanced security protocols to protect users’ assets.
- High Uptime: With an uptime guarantee of 99.9%, Allnodes ensures that staked assets are always active, maximizing reward potential.
- Transparent Fee Structure: Allnodes charges a flat fee for its services, providing predictability and stability in costs.
- Support for Multiple Cryptocurrencies: The platform supports staking across 76 PoS blockchains, allowing users to diversify their staking portfolio.
Integrating EigenLayer with Allnodes
Users can further optimize their staking strategy by integrating EigenLayer with Allnodes. This synergy allows stakers to leverage Allnodes’ secure and user-friendly platform while utilizing EigenLayer’s innovative solutions for additional rewards and enhanced security.
Conclusion
Staking represents a promising opportunity for earning passive income in the ever-evolving world of cryptocurrency. By understanding the mechanics of staking, recognizing the potential risks, and adopting strategies to maximize rewards, investors can make informed decisions that enhance their returns. Platforms like Allnodes and EigenLayer offer powerful solutions that simplify the staking process and provide innovative ways to increase earnings. As the DeFi space continues to expand, staking will likely remain a big part of the cryptocurrency investment landscape, offering attractive opportunities for those willing to explore and engage with this dynamic field.


























