Until recently, decentralized exchanges (DEXs) played a minimal role in the crypto exchanges. Centralized exchanges (CEXs) offered traders faster transaction time and higher liquidity. Although they had a limited number of tokens to trade, CEXs were the preferred option.
This changed with the arrival of PancakeSwap, a DEX that allowed everyday traders to buy tokens from new, unknown projects. With PancakeSwap and Binance Smart Chain, upcoming projects could list their tokens immediately and circumvent CEXs. Such platforms also made it possible to add liquidity to one’s token, creating thousands of new tokens for those looking to trade beyond the confines of CEXs.
However, CEXs typically have better liquidity and can handle larger transaction volumes than DEXs. Although some DEXs like PancakeSwap have a lot of liquidity, it still only executes orders using the current market price. In such a system, the time between when an order is placed and when an order is executed is not taken into account. The market price on the given token can fluctuate during this gap and traders can suffer losses.
Mate, a new DEX with a unique limit order process, aims to fix these problems.
What is Mate and How Does it Work?
Mate is a DEX designed to combat slippage and high liquidity while giving its traders the best exchange rates on all BSC assets. Besides limit orders, they also have liquidity pools and various staking options.
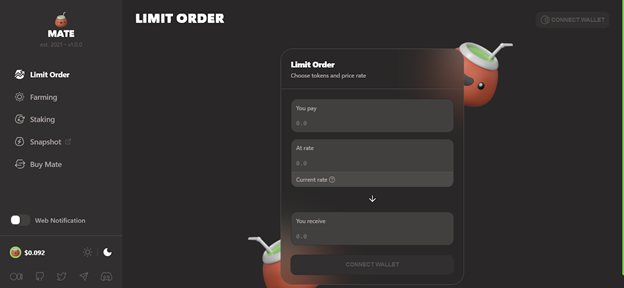
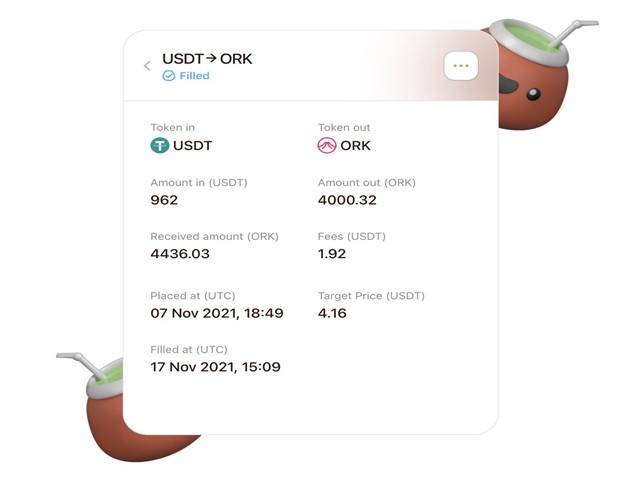
Here’s how Mate limit orders work. Users make limit orders with token pairs and set a time limit. Next, executor nodes track market activity as per the smart contract. Once the conditions are met, the executor nodes fulfill the order on an automated market maker (AMM) like PancakeSwap. The order is fulfilled at the right moment so that the final price meets the required price.
What Makes Mate Unique?
Instead of the traditional schema, Mate’s executor nodes fulfill transactions at the best moment, giving traders the best possible exchange rate. Mate takes advantage of AMMs like PancakeSwap to get enough liquidity for even the biggest trades. Since executor nodes are decentralized, limit orders are never stored on any central network. Mate’s own decentralized networks make sure orders always get fulfilled.
Executor nodes will always fulfill orders as long as the order fee rewards are more than the executor’s gas fee.
Low Fees and Refunds
Compared to other DEXs, Mate has extremely low transaction fees. Only 0.2% for limit orders. What’s more, Mate traders can enjoy BSC’s low general transaction fees. It’s possible to cancel limit orders if they haven’t yet been fulfilled or expired. Fees are refunded once the order is canceled.
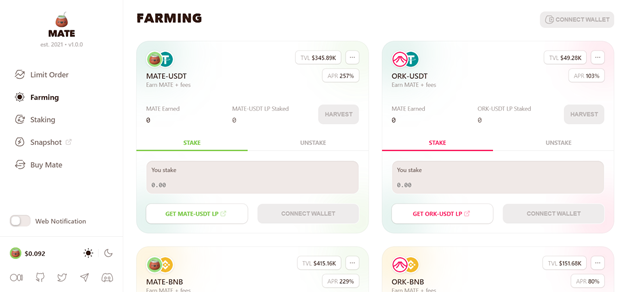
Liquidity Pool Farming
Mate also offers liquidity pool farming on their aptly named “Farm”. Anyone can earn MATE on the Farm or become a liquidity provider by staking LP tokens. The APY on LP farms is usually higher than on staking pools. LP farming APY includes staking rewards and fees from liquidity provider activity.
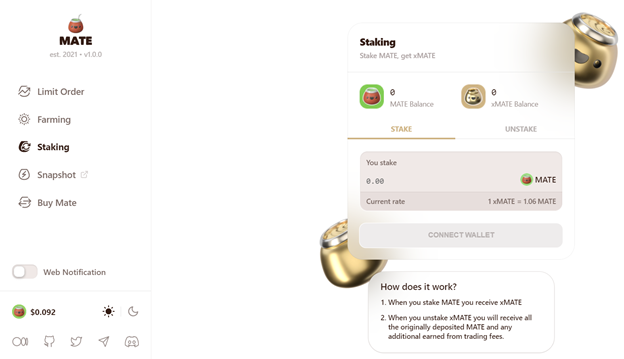
Staking Incentives
Mate also has incentives to entice users to use their services and grow their platform. When users stake MATE tokens they receive an xMATE token. Every time a limit order is made, a 0.2% fee is charged to the traders and 0.05% is sent as xMATE to stakers. The xMATE reward corresponds to the amount of staked MATE.
Mate is fully decentralized. This means that you have complete control of your crypto assets at all times. Limit orders are non-custodial, meaning your assets aren’t transferred from your wallet until the transaction actually takes place. Unlike CEXs, you keep your wallet address, it isn’t stored on any central database.
Conclusion
Mate is a bold solution to DEX’s persistent slippage and liquidity problems. Its community continues to grow and attract more investors every day. With plans to go multi-chain in the near future, the sky’s the limit for Mate.













